(13_Phunkod/Shutterstock)
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is now an accepted part of the generative AI (GenAI) workflow and is widely used to feed custom data into foundation AI models. While RAG works, calls to outside tools can add complexity and latency, which is what led the folks at MongoDB to work with in-database technology to speed things up.
As one of the most popular databases on the planet, MongoDB has developed integrations to support LangChain and LlamaIndex, two popular tools that developers use to build GenAI applications. Developers can also use any external vector database they want to store vector embeddings, indexes, and power queries at runtime.
“There’s of a multitude of ways” to build RAG workflows, says Benjamin Blast, director of product for MongoDB. “But in essence, it’s just adding friction. As a developer, I’m now responsible for finding an embedding model, procuring access to it, monitoring it, metering it — everything associated with pulling in some new component of the stack.”
While MongoDB users have options, the options are not all equal, Blast says. Anytime you go outside of the database, you’re adding friction and latency to the workflow, he says, and a bigger surface areas is also more complex to monitor and fix when things go wrong.
“We see ton of confusion and complexity in the overall market about kind of how to build these systems and how to string things together,” Blast says. “So we’re looking to dramatically simplify that.”
MongoDB wants to simplify things by building more of what GenAI developers need for RAG directly into its database. The company added a vector store by way of the Atlas Vector Search functionality in the fourth quarter of 2023. And earlier this year, it made another big move toward simplification in February when it acquired a company called Voyage AI.
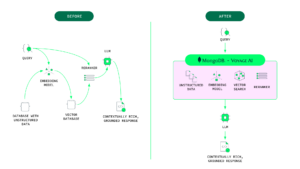
MongoDB says its integration of Voyage AI embedding and reranking models will lead to simpler GenAI architectures (Image courtesy MongoDB)
Voyage AI developed a series of embedding and reranking models designed to accelerate information retrieval in GenAI workloads and improve the overall performance of the apps. These models are offered on Huggingface and are considered to be state-of-the-art.
The Voyage AI embedding models work hand in hand to convert source data into vector embeddings that are stored in the MongoDB vector store. Voyage AI developed a range of embedding models for specific use cases and even specific domains.
“They have a range of embedding models that are of different sizes, that let you choose how good are the results going to be,” Blast tells BigDATAwire in a recent interview. “And then we let you also choose to use what are called domain-specific models, which are fine-tuned on industry specific data, so you can have one for code or one for finance or one for law, so it’ll be even better results on that.”
The Voyage AI reranking models, meanwhile, continuously optimizes the embeddings to ensure the highest accuracy during runtime, for both text and image models. These models boost performance by analyzing the vector queries and responses, and assessing which ones are the best. It will then rerank the queries and the answers (i.e. the pre-created vector embeddings) to ensure the best ones are near the top.
“That will reorder the result set and give you the highest accuracy by giving you another 5% to 7% of performance around accuracy for that result,” Blast says.
The combination of the embedded vector store and the Voyage reranking and embedding models help customers to tune their RAG workflows to ensure their foundation models are getting the data they need to provide good decisions in a timely manner.
“We can do more clever things around the integration to improve the accuracy of the results past just what the models give on their own,” Blast says. “We can make really selective improvements to that overall workflow, from the embedding model to the database to the index, that our customers just would either have a lot of trouble doing and would require a bunch of complexity, or would be fundamentally unable to do on their own.”
MongoDB is currently bringing the vector store and Voyage AI models to MongoDB Atlas, its managed database offering running in the cloud. Vector search will eventually be made available as open source; the company hasn’t determined if Voyage AI models will also be made available as open source, Blast says. Customers can also use the Voyage AI models with LangChain and LlamaIndex if they like.
MongoDB is a notoriously developer-friendly database. Other databases will likely follow its lead in building these types of specialized embedding and reranking models directly into the database. But for now, the New York company is happy to lead in this department.
“We’ve taken, I think, a pretty unique approach that gives customers the benefit of integration,” Blast says. “You get to take advantage of the same set of drivers and other capabilities to make it really easy to use, but on the back end, still scale independently, which is one of the real advantages of MongoDB.”
Related Items:
MongoDB 8.0 Release Raises the Bar for Database Performance
IBM to Buy DataStax for Database, GenAI Capabilities
MongoDB Automates Resharding, Adds Time-Series Support
July 15, 2025
- Nutanix Survey Finds Financial Firms Embracing GenAI but Struggling with Skills Gaps
- Qdrant Launches Qdrant Cloud Inference to Unify Embeddings and Vector Search Across Multiple Modalities
- Data Axle Reveals Most Brands Still Rely on Fragmented Customer Data
- Cyberlocke Expands Data Assurance Platform with New DQS Framework
- Coralogix Introduces MCP Server to Help Customers Build Smarter AI Agents
- Forrester’s 2026 Budget Planning Guides: Leaders Grow More Cautious As Economic Uncertainty Persists
- Open Flash Platform Initiative Unveiled by Industry and Research Leaders
- Collate Raises $10M Series A to Solve the Data Intelligence Challenges for Enterprise Customers
- TigerGraph Secures Strategic Investment to Advance Enterprise AI and Graph Analytics
- Seagate Launches 30TB Drives to Power AI and Edge Workloads
July 14, 2025
- Esri’s ArcGIS Basemaps Power Dataminr First Alert for Enhanced Real-Time Event Detection and Awareness
- Hyland Launches Knowledge Enrichment to Turn Unstructured Content into AI-Ready Data
- AWS Launches EC2 UltraServers Powered by NVIDIA Grace Blackwell
- Esri Collaborates with Microsoft to Bring ArcGIS Users New AI Enhancements
July 11, 2025
- NVIDIA: AI-Powered Climate Models Go Mainstream
- RealSense Completes Spinout from Intel, Raises $50M to Accelerate AI-Powered Vision
- Emory University: Exploring the Frontiers of Data Science, Across Space and Time
- Anaconda Announces Partnership with Prefix.dev to Bring Next-Gen Functionality to conda-build
- Amplitude Acquires Kraftful to Accelerate AI Strategy
- Astronomer and AWS Announce Strategic Collaboration Agreement
- Inside the Chargeback System That Made Harvard’s Storage Sustainable
- LinkedIn Introduces Northguard, Its Replacement for Kafka
- What Are Reasoning Models and Why You Should Care
- Databricks Takes Top Spot in Gartner DSML Platform Report
- Scaling the Knowledge Graph Behind Wikipedia
- Top-Down or Bottom-Up Data Model Design: Which is Best?
- Iceberg Ahead! The Backbone of Modern Data Lakes
- Four Steps for Turning Data Clutter into Competitive Power: Your Sovereign AI and Data Blueprint
- Fine-Tuning LLM Performance: How Knowledge Graphs Can Help Avoid Missteps
- What Is MosaicML, and Why Is Databricks Buying It For $1.3B?
- More Features…
- Mathematica Helps Crack Zodiac Killer’s Code
- Supabase’s $200M Raise Signals Big Ambitions
- Solidigm Celebrates World’s Largest SSD with ‘122 Day’
- Confluent Says ‘Au Revoir’ to Zookeeper with Launch of Confluent Platform 8.0
- Data Prep Still Dominates Data Scientists’ Time, Survey Finds
- With $17M in Funding, DataBahn Pushes AI Agents to Reinvent the Enterprise Data Pipeline
- AI Is Making Us Dumber, MIT Researchers Find
- ‘The Relational Model Always Wins,’ RelationalAI CEO Says
- The Top Five Data Labeling Firms According to Everest Group
- Toloka Expands Data Labeling Service
- More News In Brief…
- Gartner Predicts 40% of Generative AI Solutions Will Be Multimodal By 2027
- Seagate Unveils IronWolf Pro 24TB Hard Drive for SMBs and Enterprises
- Campfire Raises $35 Million Series A Led by Accel to Build the Next-Generation AI-Driven ERP
- BigBear.ai And Palantir Announce Strategic Partnership
- Databricks Announces Data Intelligence Platform for Communications
- Deloitte Survey Finds AI Use and Tech Investments Top Priorities for Private Companies in 2024
- Gartner Predicts 30% of Generative AI Projects Will Be Abandoned After Proof of Concept By End of 2025
- Code.org, in Partnership with Amazon, Launches New AI Curriculum for Grades 8-12
- Gartner Predicts Over 40% of Agentic AI Projects Will Be Canceled by End of 2027
- NIH Highlights AI and Advanced Computing in New Data Science Strategic Plan
- More This Just In…